Fleet Maintenance Audit Checklist
A fleet maintenance audit checklist is a structured method used to verify whether vehicles, maintenance processes, documentation, and compliance controls are operating as intended. Regular audits help fleets identify gaps early, reduce operational risk, and maintain consistent safety and cost control standards.

Fleet Maintenance Audit Areas and Evidence
| Audit Area | What to Verify | Evidence to Collect | Common Finding Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preventive Maintenance | Schedule adherence | PM logs and reminders | Overdue services |
| Work Orders | Authorization and closure | Repair records | Missing approvals |
| Inspections | Driver and mechanic checks | DVIR forms | Unresolved defects |
| Parts Inventory | Stock and warranty tracking | Inventory reports | Stockouts |
| Compliance Records | Regulatory documentation | Certificates and reports | Expired documents |
Internal Self-Audit vs External Audit Preparation

Internal Self-Audit
- Conducted by internal staff or managers
- Focused on process improvement and early gap detection
- Flexible sampling and timing
- Findings typically used for corrective planning

External Audit Preparation
- Conducted by regulators, insurers, or third parties
- Focused on formal compliance validation
- Strict documentation and traceability expectations
- Findings may result in penalties or mandated actions
Audit Scope, Standards, and Evidence
A maintenance audit must begin with clearly defined scope and reference standards. Without boundaries and defined evidence expectations, audits become inconsistent and difficult to repeat or benchmark.
- Identify fleet size, vehicle types, and asset categories included
- Define applicable regulations, OEM requirements, and internal policies
- Establish sampling percentages for vehicles and records
- Determine acceptable evidence formats (digital, paper, system logs)
- Align audit frequency with operational risk levels
Outcome Gist:
- Clear boundaries
- Repeatable structure
- Comparable audit results


Maintenance Program Controls
Program controls ensure that preventive and corrective maintenance activities are performed consistently and approved through defined channels. Weak control systems often lead to overdue maintenance or undocumented repairs.
- Verify preventive maintenance schedules match OEM or policy standards
- Review work order approval flows and closure validation
- Confirm vendor and shop accountability procedures
- Check escalation paths for urgent or safety-critical repairs
- Assess maintenance reminder reliability and notification accuracy
Outcome Gist:
- Predictable maintenance flow
- Reduced service delays
- Strong accountability chain
Records, Documentation, and Traceability
Documentation is the foundation of audit readiness. Incomplete or scattered records are among the most common audit failures across fleets of all sizes.
- Confirm vehicle service history completeness and chronological order
- Validate inspection records and defect resolution trails
- Review parts inventory logs and warranty documentation
- Ensure mileage and usage logs align with maintenance timing
- Check document retention policies and backup procedures
Outcome Gist:
- Strong audit trail
- Faster verification
- Reduced compliance risk


Safety and Compliance Readiness
Safety and compliance checks evaluate whether vehicles are roadworthy and whether drivers and managers follow required inspection and reporting practices.
- Verify driver inspection routines and follow-through actions
- Confirm out-of-service criteria are documented and enforced
- Review compliance certificates, emissions tests, and safety reports
- Evaluate reporting dashboards and management review frequency
- Assess training records for drivers and maintenance staff
Outcome Gist:
- Improved road safety
- Reduced regulatory exposure
- Higher operational confidence
Final Takeaways
Fleet maintenance audits are not isolated compliance exercises; they are operational health checks that improve reliability and cost control when performed consistently.
- Define clear audit scope and evidence standards before starting
- Verify maintenance controls, not just paperwork
- Maintain centralized and chronological service documentation
- Treat driver inspections as a critical safety input
- Schedule audits regularly rather than reactively
AUTOsist Fleet Management Resources

Fleet Compliance Guide

Vehicle Inspection Guide
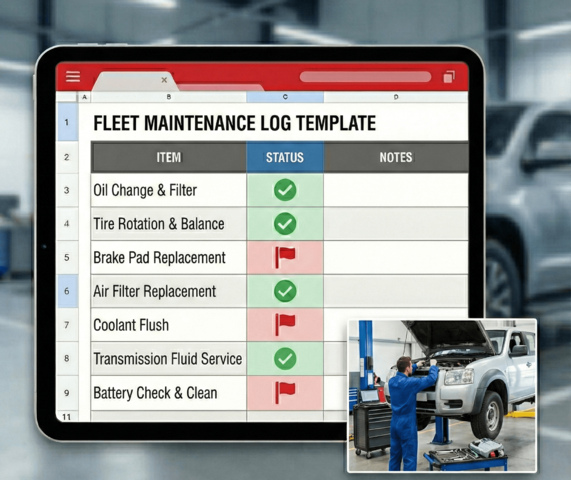
Fleet Maintenance Log Excel Template
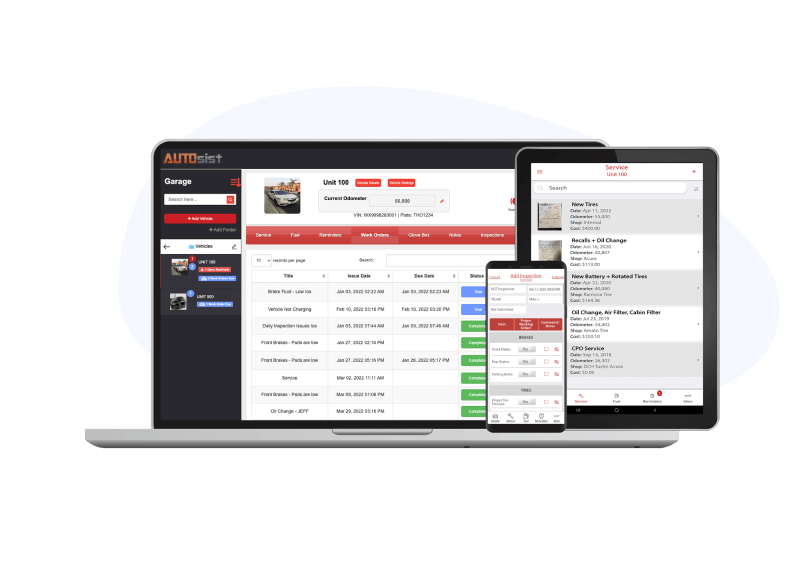
Fleet Maintenance Software