DOT Fleet Maintenance Requirements Explained
DOT fleet maintenance requirements establish the minimum standards fleets must follow to ensure vehicles are safe, inspected regularly, repaired promptly, and supported by verifiable records. For fleet managers and maintenance teams, these rules are less about paperwork and more about maintaining consistent vehicle condition, operational safety, and audit-ready proof of compliance.

DOT Maintenance Requirements at a Glance
| Requirement Area | What DOT Expects | Primary Owner | Typical Proof |
|---|---|---|---|
| Systematic Maintenance | Ongoing inspection, repair, and upkeep program | Maintenance Team | Service schedules, work orders |
| Driver Vehicle Inspections | Daily pre/post-trip checks | Drivers | DVIR reports |
| Defect Repair & Closeout | Timely correction of safety defects | Maintenance / Ops | Repair records, verification notes |
| Recordkeeping | Organized retention of maintenance data | Operations | Digital or paper logs |
| Audit Readiness | Ability to present evidence on demand | Fleet Manager | Consolidated reports |
Minimum Compliance vs. Audit-Ready Operations

Minimum Compliance
- Maintenance occurs but schedules may be inconsistent
- Records exist but are scattered across spreadsheets or paper files
- Defects are repaired, yet verification documentation is limited
- Audit preparation is reactive rather than continuous

Audit-Ready Operations
- Preventive schedules are defined and automatically tracked
- Records are centralized and searchable by vehicle or date
- Defect reports link directly to repair completion evidence
- Compliance reviews are routine rather than emergency responses
Scope and Applicability of DOT Maintenance Rules
DOT maintenance obligations generally apply to commercial motor vehicles operating in interstate commerce or meeting defined weight and passenger thresholds. Understanding applicability prevents both over-engineering and under-compliance.
Before creating or revising maintenance programs, fleets typically evaluate:
- Vehicle weight classifications and usage types
- Passenger capacity and cargo categories
- Interstate versus intrastate operations
- Contractual or customer safety requirements
- Insurance and risk management expectations
Operational outcomes:
- Clear determination of which vehicles fall under DOT rules
- Alignment between legal scope and maintenance resources


Required Maintenance Program Elements
DOT regulations emphasize a systematic approach rather than ad-hoc repairs. Fleets must demonstrate that inspections, servicing, and defect corrections follow a repeatable structure.
Core elements of a compliant program often include:
- Documented preventive maintenance schedules by vehicle type
- Defined inspection intervals based on mileage or hours
- Formal work order or repair authorization processes
- Assigned accountability for inspection and repair decisions
- Verification that safety-critical defects are corrected before operation
Operational outcomes:
- Reduced unplanned downtime
- Improved traceability of maintenance decisions
Recordkeeping and Documentation Expectations
Documentation is the primary evidence of compliance. DOT does not only expect maintenance to occur; it expects fleets to prove that it occurred within required timeframes.
Typical recordkeeping practices include:
- Vehicle service histories with dates and mileage
- Inspection reports linked to repair actions
- Parts replacement logs and warranty notes
- Retention policies tied to vehicle lifecycle status
- Organized digital or indexed physical storage systems
Operational outcomes:
- Faster audit responses
- Improved internal accountability and historical analysis


Driver Inspections and Vehicle Condition Control
Driver Vehicle Inspection Reports (DVIRs) act as the frontline detection system for safety issues. The effectiveness of DVIRs depends on whether reported defects move efficiently into repair workflows.
Common control practices involve:
- Standardized pre-trip and post-trip inspection checklists
- Clear guidance on what constitutes a safety defect
- Immediate reporting channels for critical issues
- Maintenance verification signatures or digital confirmations
- Supervisory review of unresolved inspection items
Operational outcomes:
- Early identification of mechanical risks
- Better communication between drivers and technicians
Audit Readiness and Operating Controls
Audit readiness is not a separate activity; it is the by-product of consistent daily controls. Fleets that maintain structured reviews are less likely to face compliance gaps.
Typical operating controls include:
- Monthly internal record audits for completeness
- Quarterly maintenance schedule reviews
- Random DVIR sampling and verification checks
- Technician training refreshers on documentation standards
- Consolidated reporting dashboards for oversight
Operational outcomes:
- Lower compliance stress during external reviews
- Continuous improvement in maintenance discipline

Final Takeaways
DOT fleet maintenance requirements focus on consistency, documentation, and verifiable safety controls rather than one-time compliance efforts.
- Determine clearly which vehicles and operations fall under DOT scope.
- Build repeatable maintenance schedules instead of reactive repairs.
- Centralize records so proof is immediately available.
- Link driver inspections directly to repair verification.
- Treat audit readiness as an ongoing operational habit, not an event.
AUTOsist Fleet Management Resources

Fleet Compliance Guide

Preventative Maintenance Guide for Fleet Operations
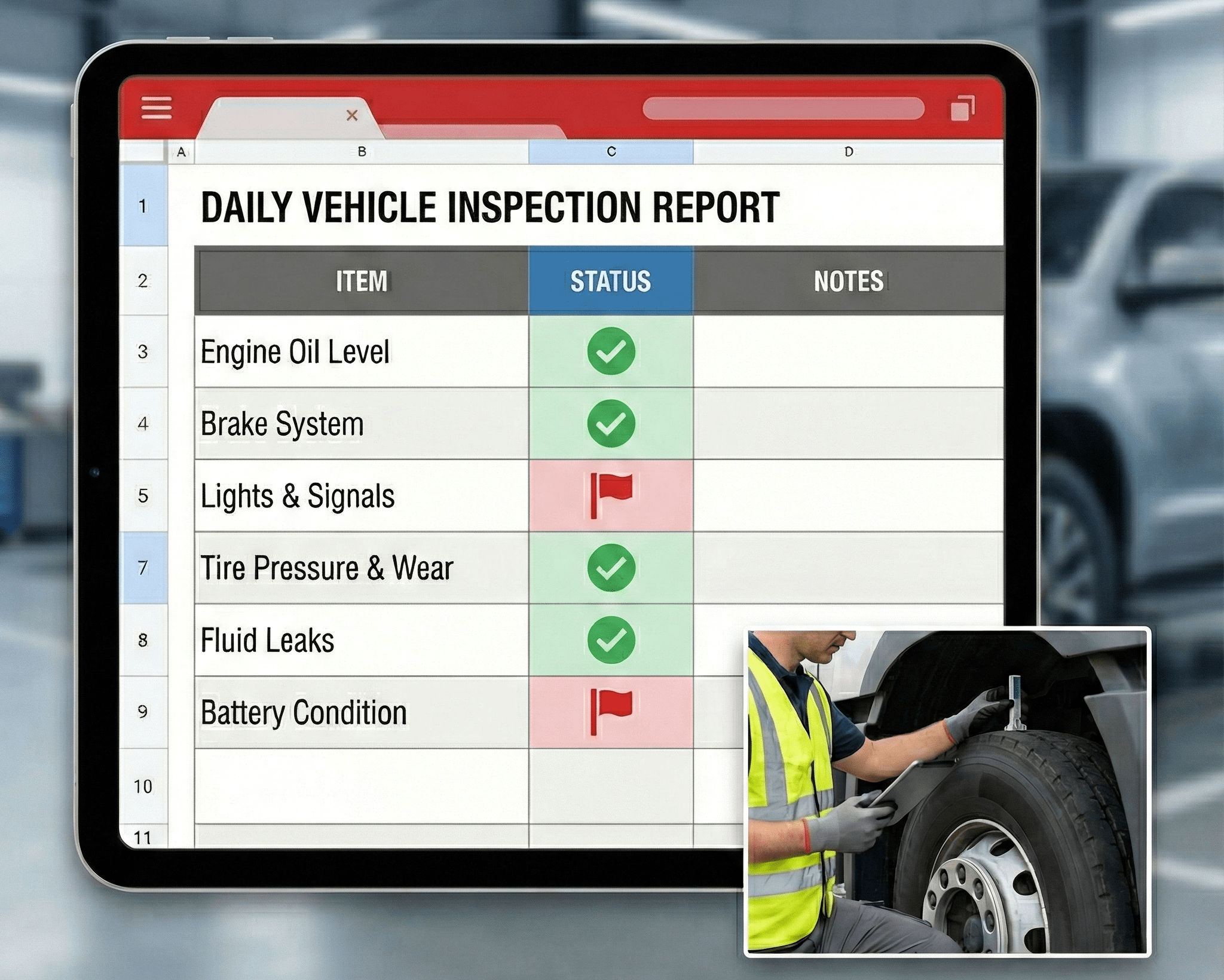
Daily DVIR Vehicle Inspection Checklist PDF
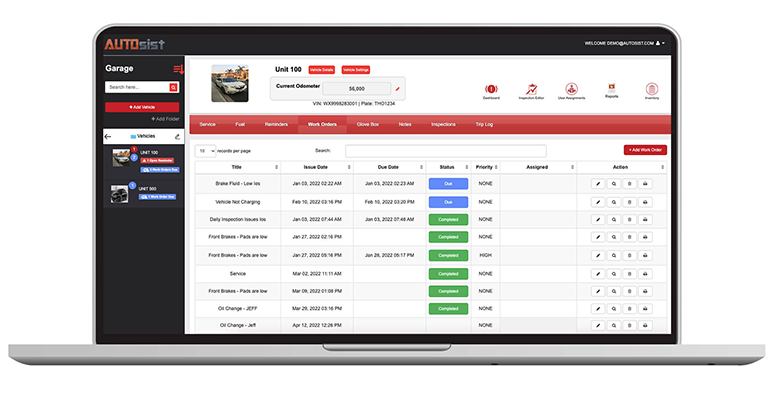
Fleet Maintenance Work Order Software